How Do Fish Breathe?
zygotehasnobrain/iStock / Getty Images Plus via Getty Images
Fish breathe underwater by pumping water over their gills, where oxygen is extracted through a highly efficient system called countercurrent exchange.
Fish need oxygen just like all animals do—yet they live in an environment where oxygen is far less abundant than in air. To survive, fish evolved gills capable of pulling small amounts of dissolved oxygen out of water with remarkable efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Fish breathe using gills, specialized organs that extract small amounts of dissolved oxygen from water.
- Countercurrent exchange allows fish to absorb oxygen efficiently by running blood opposite the flow of water.
- Water contains far less oxygen than air, which is why fish require such an efficient respiratory system.
- Healthy aquarium conditions (good filtration, proper aeration, stable water chemistry) are essential for normal fish respiration.
Do Fish Breathe?
Yes, fish breathe in oxygen from the water—just not the same way humans and other land animals breathe.
Humans and fish both need oxygen delivered to cells throughout the body to maintain normal function. Humans use lungs to draw in oxygen from air, while fish use gills to get oxygen from the water. Once the gills take in oxygen from the water, that oxygen binds to red blood cells, which deliver the oxygen to the rest of the body.
How Do Fish Breathe Underwater?
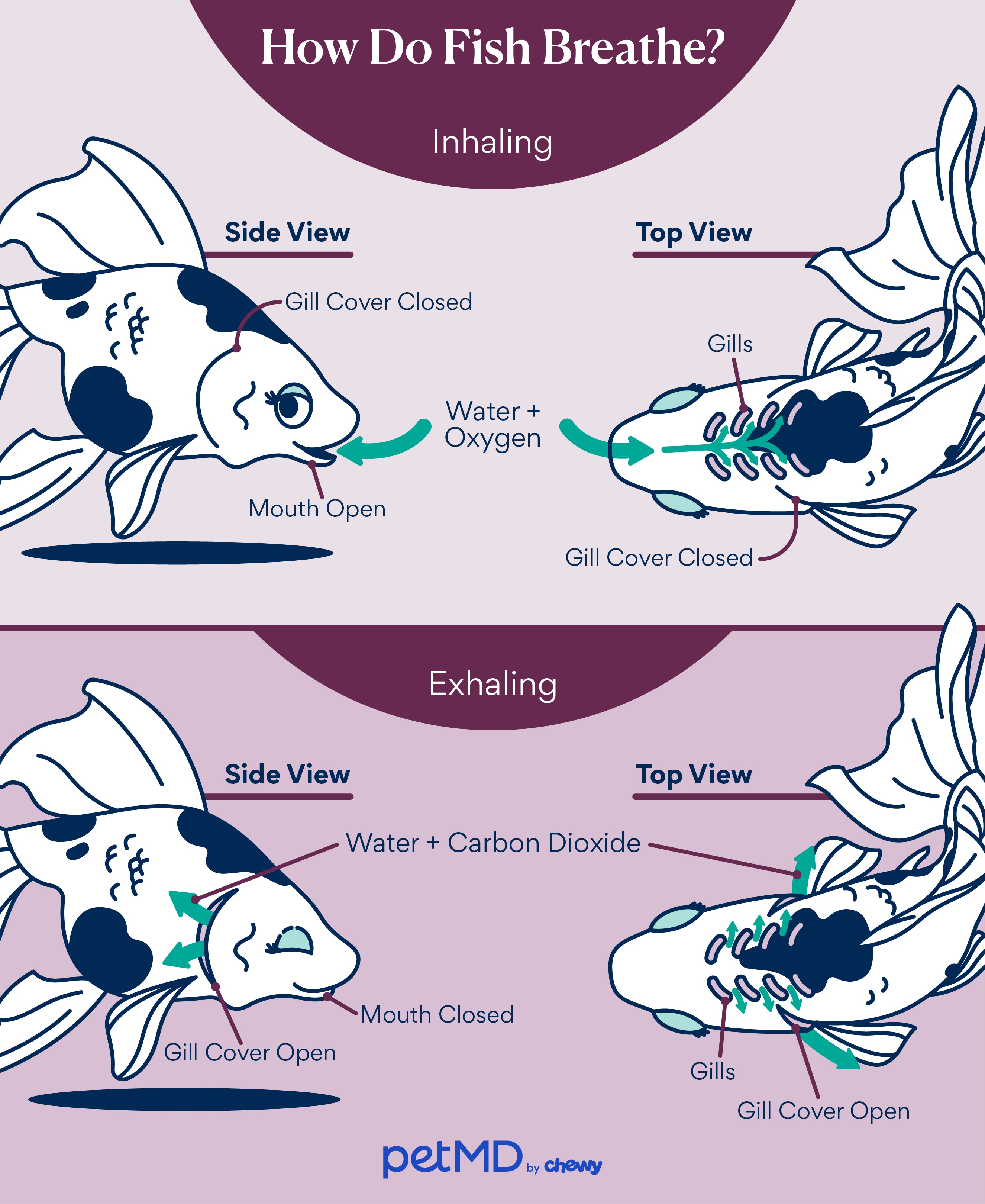
Fish have gills located behind the operculum, a plate-like covering that helps water move over the gills.
Gills are designed to move water through a countercurrent exchange system that helps the fish absorb oxygen from the water.
Here’s how fish breathing works:
-
Water directed by the operculum (gill cover) flows in through the mouth and over the gills.
-
The operculum opens and closes, which moves water over the gills.
-
Water then courses over the gill arches. Gill arches are a part of the primary respiratory organ of the fish.
-
Water is exposed to the gill filaments, which are made up of lamellae (thin filaments that are responsible for gas exchange in the fish’s body). The oxygen is absorbed in the lamellae.
-
Blood containing minimal oxygen will flow in the opposite direction of the water flow around the fish in small blood vessels within the lamellae.
-
As the blood flows against the water flow, it collects more oxygen until it reaches its maximum oxygen content.
-
Blood with oxygen is pumped into systemic circulation to deliver oxygen to the fish’s organs.
Once the water has crossed the gills, the oxygen content decreases. Gases like carbon dioxide and other metabolic waste products are passed into the surrounding water.
Trouble Breathing in Fish
Proper fish breathing is essential; if a fish is unable to obtain oxygen from the water, it can lead to life-threatening diseases and even sudden death.
Fish can develop diseases in their gills such as parasitic and viral infections, which can be fatal.
One of the first signs of gill disease if a fish is open-mouth breathing at the surface. This behavior indicates the fish are trying to get oxygen from air because they are unable to breathe in the water.
If your fish is having these issues, ensure that all of the life support for your home aquarium is working correctly and then check the water quality, including dissolved oxygen content. If all of these are normal, seek out a veterinarian who specializes in fish.
Fish Breathing FAQs
Why can’t fish breathe on land?
Most fish are unable to breathe air on land because they are unable to move air over their gills in an efficient manner to successfully obtain oxygen. However, some fish species can survive on land for short periods of time, and some fish, such as the Mudskipper, can breathe air.
Do fish have to keep swimming to breathe?
Not all fish breathing requires constant swimming. Often, the movements of the operculum alone allow a fish to move enough water over their gills to breathe. However, some fish species require constant flow over their gills, which means moving all the time.
Does water hold more or less oxygen than air?
Water holds on to less oxygen than air. The air that humans breathe at sea level contains about 21% oxygen, while water, depending on a variety of factors like water temperature and atmospheric pressure, can range from 0.49% to 0.8% oxygen. This is one of the reasons why fish gills are designed to be efficient at extracting oxygen from water.
