Swollen Gums in Dogs
Gingivitis in Dogs
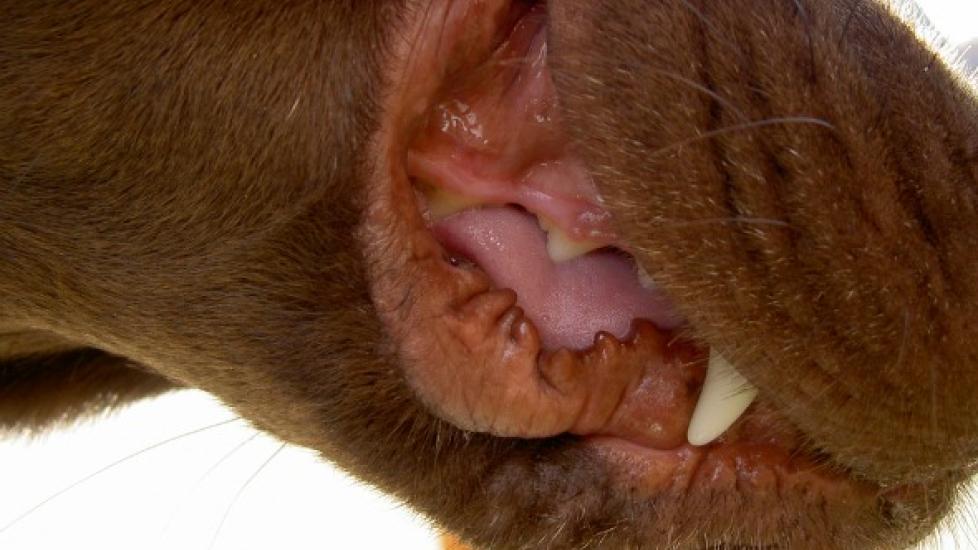
Gingivitis is a reversible inflammation of the gums and is considered the earliest stage of periodontal disease. In the early phases of gingivitis, some plaque is present and there is a mild redness of the gums, but the gingival surfaces are smooth.
The gingival sulcus, or gum pocket, is the narrow space between the inner wall of the gum and the tooth. As gingivitis develops, the bacteria present in these pockets changes for the worse, and the accumulation of more bacteria, which release toxins, destroy gums.
In advanced gingivitis there is plaque and calculus under the gums, moderate-to-severe redness of the gums, and the gum surfaces are irregular. Dental calculus is calcium phosphate and carbonate mixed with organic matter, while plaque is a collection of food, debris, bacteria, dead skin cells, and mucous that forms within 24 hours on clean tooth surfaces. The gum responds to plaque with an inflammation of blood vessels, swelling, and collagen loss.
More than 80 percent of pets three years or more of age have gingivitis. It develops earlier in life in toy breeds, and in general, affects dogs earlier in life than it does cats.
Symptoms and Types
- Red or swollen gums, especially on the side of the gum facing the inner cheeks
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Variable amounts of plaque and calculus
Causes
Plaque accumulation is one of the main causes leading to gingivitis in dogs. Predisposing factors include:
- Old age
- Crowded teeth
- Soft food
- Open-mouth breathing
- Bad chewing habits
- Lack of oral health care
- Uremia and diabetes mellitus
- Automimmune diseases
Diagnosis
Your veterinarian will perform a thorough physical exam on your dog, taking into account the background history of symptoms and possible conditions that might have led to this condition. You will need to give a thorough history of your dog's health and onset of symptoms, such as when the bad breath began, what your dog typically eats, whether your dog has had trouble eating/chewing, and whether your dog has had any previous health conditions. The routine you have been using to keep your dog's teeth clean, if you have been using one, should be shared with your veterinarian as well, including the products you use.
Part of the physical exam involves closely examining your dog's mouth to identify the condition. Your veterinarian will then make an appointment with you to bring your dog in for a dental exam. During the dental exam, your dog will be anesthetized. Your veterinarian will check the depth of the gum pockets, the amount of plaque and bacteria on the surface of the teeth, and will pull any teeth that are rotten or that are too crowded. All of the plaque and calculus will be removed using a scaling process that is done with special dental equipment, and if necessary, root planning. The tooth surfaces will be polished and the teeth will be reexamined after cleaning.
Treatment
If teeth are overcrowded or baby teeth are present in an adult dog, your veterinarian may remove some teeth. Special dental tools will be used to remove all plaque and calculus, to polish the teeth, and to rinse them. He or she will then teach you how to clean your pet’s teeth, and appointments for follow-up examinations should be scheduled.
Living and Management
You can help maintain your dog’s oral health care by brushing or rubbing (with a special finger pad) its teeth once a day or at least twice a week with veterinary toothpaste. Your veterinarian may also give you a veterinary antibacterial solution to squirt on your pet’s teeth to decrease plaque build-up. Rawhide chew strips and specialized food recommended to you by your veterinarian can reduce tartar and improve the dog's oral health as well.